FlexiRemap Advantages
Enterprise IT demands data protection, storage performance, and system durability. AccelStor answers these needs.
Enhanced Data Protection
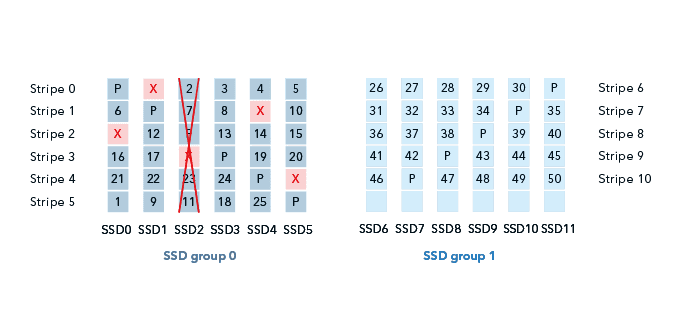
Unlike the data redundancy of conventional RAID, FlexiRemap provides a proprietary algorithm for data protection by dividing SSDs into groups. Data is evenly distributed across SSD groups, with fault tolerance of single-drive failure per group (Figure 1). Should a drive fail, FlexiRemap forwards incoming write requests to the groups without the failed SSD, keeping newly written data protected.
Enhanced Data Protection
Unlike the data redundancy of conventional RAID, FlexiRemap provides a proprietary algorithm for data protection by dividing SSDs into groups. Data is evenly distributed across SSD groups, with fault tolerance of single-drive failure per group (Figure 1). Should a drive fail, FlexiRemap forwards incoming write requests to the groups without the failed SSD, keeping newly written data protected.
Figure 1: FlexiRemap features built-in data protection
Better Performance
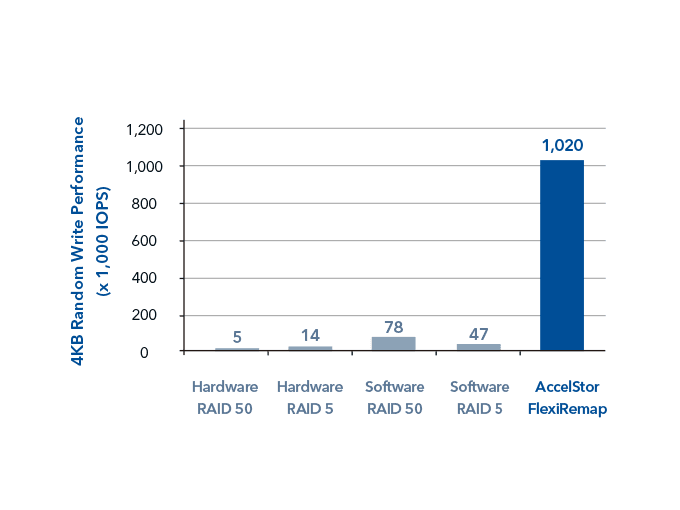
Conventional RAID systems are unable to efficiently handle large loads of I/O requests, particularly in random write mode, resulting in poor storage performance. FlexiRemap technology features an exclusive data remapping algorithm based on the physical nature of NAND flash memory. FlexiRemap reduces the workload of SSDs by enabling them to directly write sequential data into consecutive pages, which accelerates random writes. Total performance is enhanced up to 1,020K IOPS as compared with the RAID algorithm, which only generates around 5K IOPS to 78K IOPS (Figure 2).
Conventional RAID systems are unable to efficiently handle large loads of I/O requests, particularly in random write mode, resulting in poor storage performance. FlexiRemap technology features an exclusive data remapping algorithm based on the physical nature of NAND flash memory. FlexiRemap reduces the workload of SSDs by enabling them to directly write sequential data into consecutive pages, which accelerates random writes. Total performance is enhanced up to 1,020K IOPS as compared with the RAID algorithm, which only generates around 5K IOPS to 78K IOPS (Figure 2).
Figure 2: FlexiRemap vs. RAID performance in IOPS
Maximized SSD Lifespan
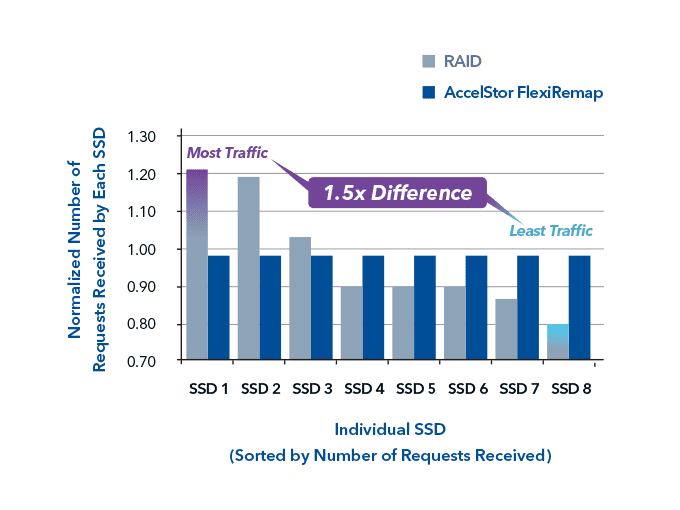
Unlike HDDs, SSDs have a finite number of program-erase (P/E) cycles. RAID does not address repeated programming and wear on flash memory. The nature of RAID is to generate repeated operations on the same locations; the frequent P/E cycles cause some SSDs to endure more loading than others. FlexiRemap's algorithm guarantees that data is evenly distributed across each SSD in every group. Evenly distributed data across SSDs not only yields better performance, but also extends SSD lifespan (Figure 3).
Unlike HDDs, SSDs have a finite number of program-erase (P/E) cycles. RAID does not address repeated programming and wear on flash memory. The nature of RAID is to generate repeated operations on the same locations; the frequent P/E cycles cause some SSDs to endure more loading than others. FlexiRemap's algorithm guarantees that data is evenly distributed across each SSD in every group. Evenly distributed data across SSDs not only yields better performance, but also extends SSD lifespan (Figure 3).
Figure 3: FlexiRemap vs. RAID: Number of requests received on SSDs
| Sans Digital Flexiremap Technology Brief |